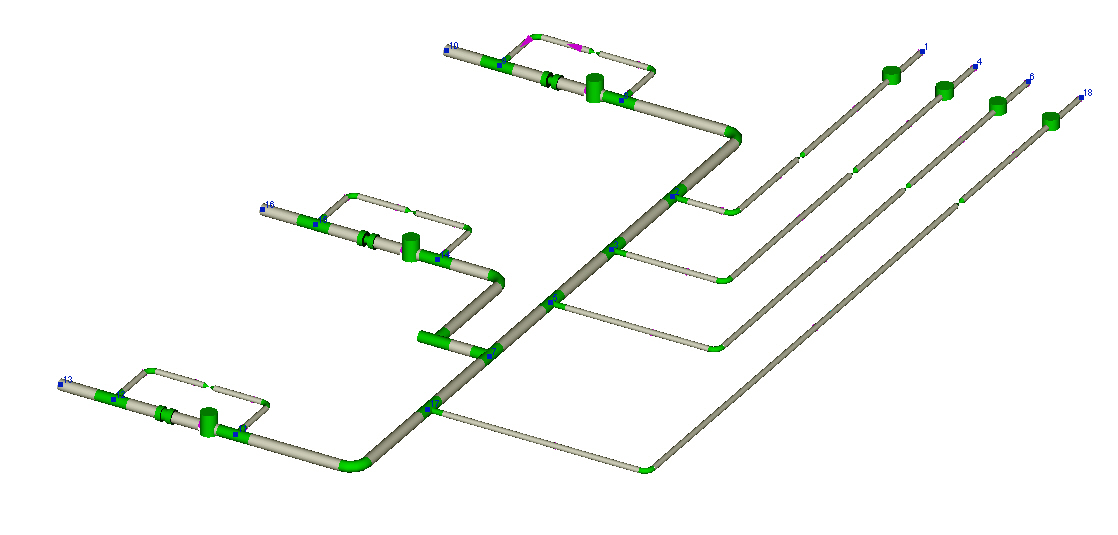
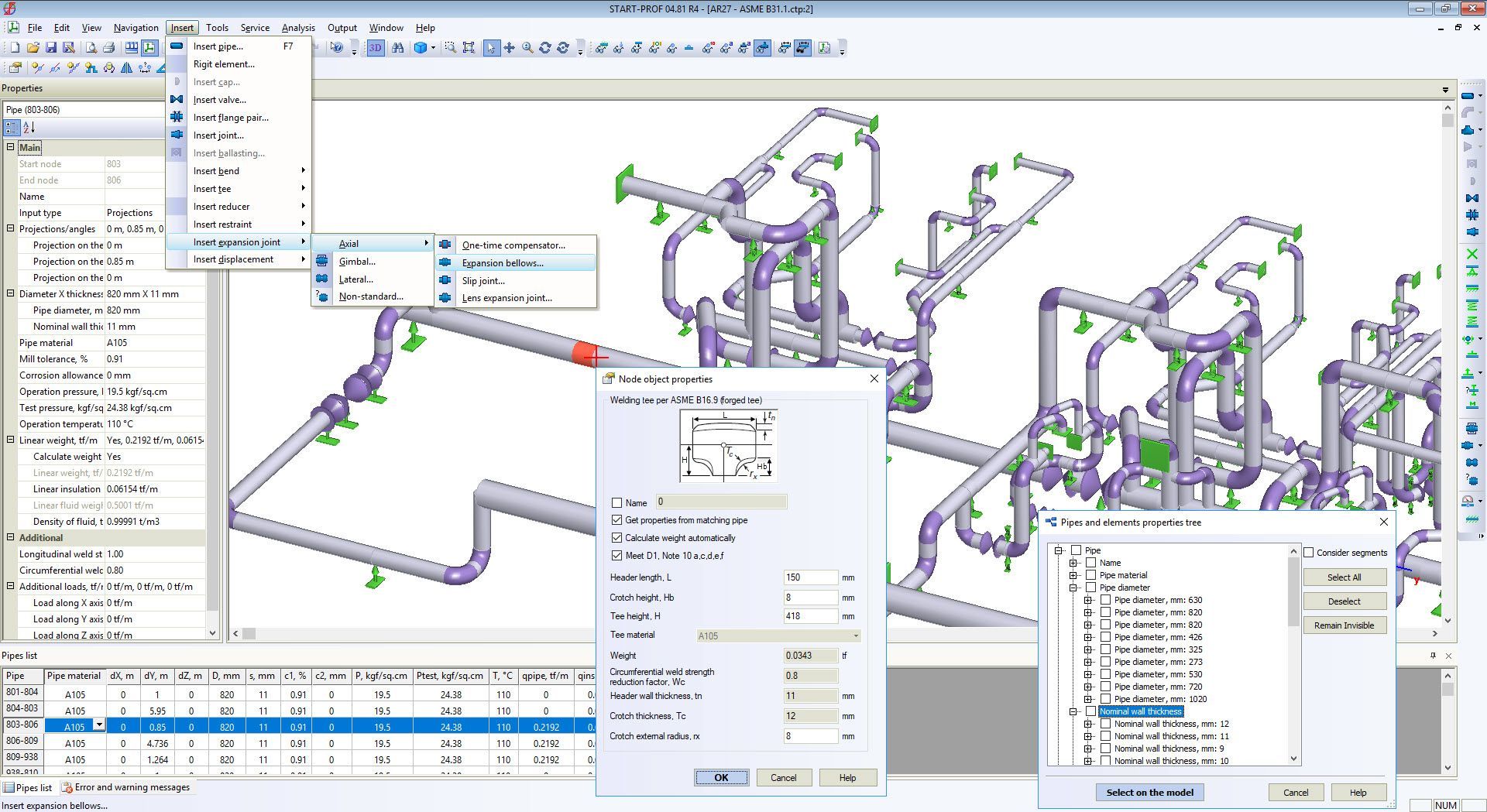
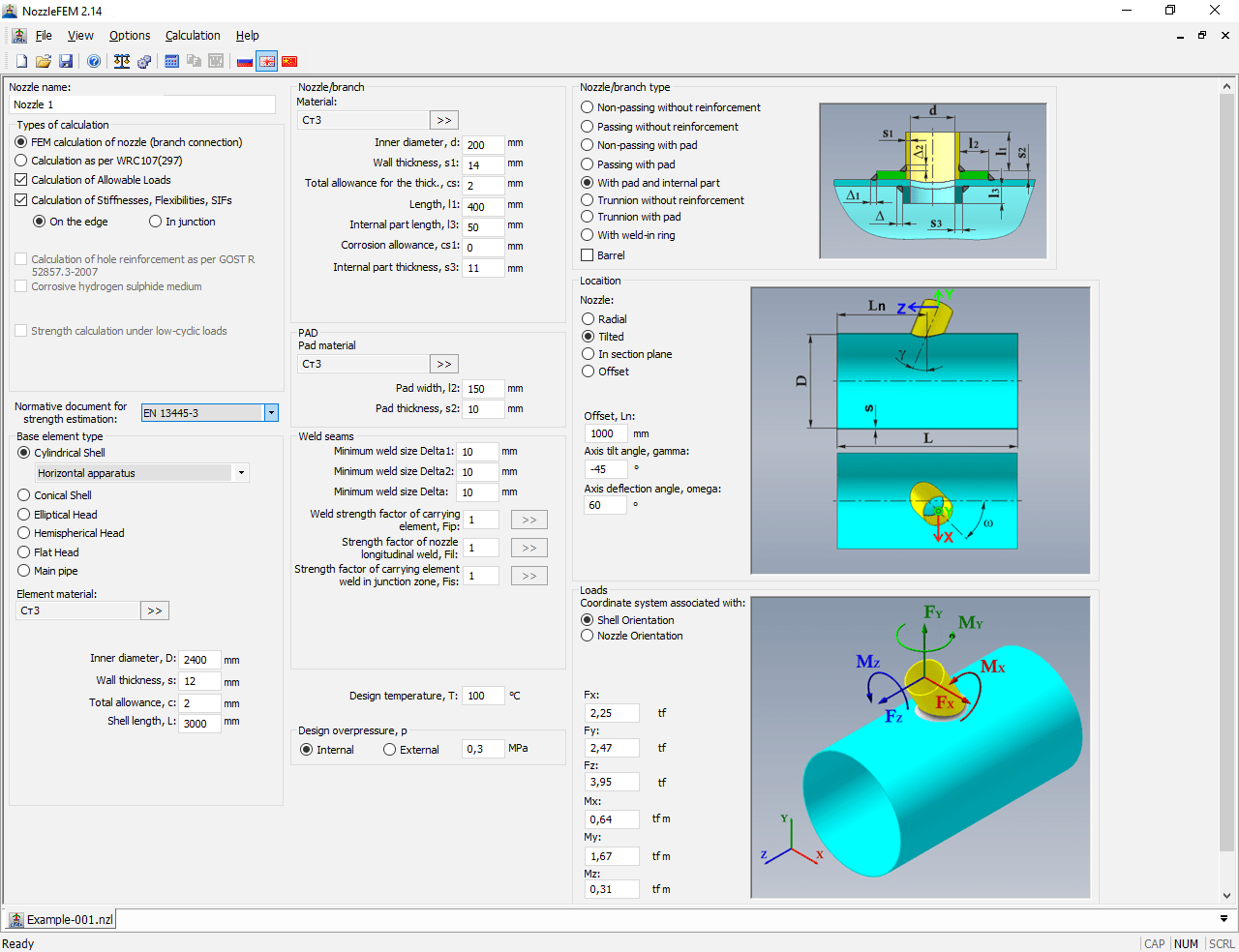
In order to analyze a piping system for hydraulic and thermal effects, it is necessary to simulate its behavior on three scale levels: pipe cross section, pipe/branch run, and the whole piping network – and then link and solve these models together.
At the cross-sectional scale, it is necessary to define the type of fluid flow (laminar, turbulent, choked, or subsonic), flow pattern for multiphase flow (stratified, annular, intermitted, etc.), and the specifics of heat exchange between fluid and the environment through pipe wall and thermal insulation. This knowledge is then used when calculating integral parameters of the flow and heat exchange (pressure gradient, heat losses per length, etc.) and following up how all fluid parameters change along the pipe/ branch and all over the network. This would be impossible without access to the most reliable thermodynamic data provided by the software.
PASS/HYDROSYSTEM provides a calculation engine for all necessary fluid properties and phase equilibrium on the basis of fluid composition, for a wide spectrum of fluids and applications.
Thermodynamics libraries used include: the advanced proprietary library for refining and petrochemical industry; the library on the base of the International Association of the Properties of Water and Steam formulation; the most accurate modern GERG-2008 library for natural gas; access to the Simulis Thermodynamics calculation server by ProSim SA (for chemical, biochemical and other industries); and PVTSim Hydrate Open Structure Library by Calsep.
PASS/HYDROSYSTEM uses the most advanced models/algorithms and libraries for all level of simulation (both proprietary and from famous researchers/developers from all over the world).
This includes minor losses correlations by Idelchik, Miller, and Ito; multiphase flow models by Chisholm, Friedel, Taitel, Barnea, and Tulsa University Fluid Flow Project research group; DHLLDV slurry flow model by Delft University of Technology; Todini Global Gradient Algorithm for network solver; Powell derivative-free method for optimization; and many others.